Exploring the Most Popular Organic Fermented Foods.
In recent years, organic fermented foods have gained significant popularity, largely due to an increased awareness of their health benefits and a growing interest in natural, sustainable eating practices. This age-old preservation method, organic fermentation, is being rediscovered for its many health perks. Foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha are not only tasty and nutritious but also packed with beneficial probiotics that are essential for gut health. Furthermore, studies suggest that these foods can greatly enhance immunity and overall wellness.
The human gut hosts a diverse array of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and yeasts. This microbiome is vital for digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune health. When the balance of gut flora is disrupted, it can lead to various health problems, such as digestive issues, autoimmune disorders, and even mental health challenges. Organic fermented foods, which are abundant in live probiotics, help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium are typically found in these foods. Research indicates that regularly consuming fermented foods can help restore gut bacteria balance, enhance digestion, alleviate symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and reduce bloating and discomfort.
Approximately 70% of the immune cells in our body are found within the gastrointestinal system. The gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) plays a crucial role in immune responses and protecting the body from infections. Consuming organic fermented foods can boost the immune system by promoting a healthy gut microbiota.
The probiotics present in these fermented foods encourage the production of immune cells, including T lymphocytes and natural killer cells, which are vital for combating infections. Studies have indicated that probiotics can also affect the generation of anti-inflammatory cytokines, aiding in the regulation of immune responses and the reduction of chronic inflammation. One particular study emphasized how certain probiotic strains can help regulate immune responses and prevent autoimmune diseases by reinforcing the gut barrier.
Fermented foods, including sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha, are packed with bioactive compounds like vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that bolster immune health. For instance, kimchi is particularly rich in vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that aids immune function, while kombucha is celebrated for its polyphenols, which possess antimicrobial and immune-enhancing qualities.
Additionally, fermented foods contain short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyrate, which play a significant role in promoting metabolic health. These SCFAs are generated by beneficial gut bacteria during the fermentation process and are known to encourage healthy inflammation, enhance insulin sensitivity, and support cognitive function. Consequently, regularly including fermented foods in your diet can lead to improved mood, increased energy, and greater mental clarity.
Furthermore, organic fermented foods can contribute to weight management. Research indicates that the probiotic strains found in these foods may assist in regulating body weight by enhancing fat metabolism and decreasing fat storage. As a result, fermented foods present a compelling choice for those looking to embrace a healthy and sustainable diet.
Kimchi: The Spicy Superfood Packed with Nutrients from Korea
Kimchi is a fundamental element of Korean cuisine, boasting a rich history that spans over two millennia. Recognized for its striking red hue, strong aroma, and spicy taste, kimchi is a fermented dish primarily made from cabbage or radishes, seasoned with a blend of chili pepper, garlic, ginger, salt, and fish sauce. The fermentation process, which utilizes beneficial bacteria, not only enhances its flavor and nutritional value but also offers various health benefits.
Originally, kimchi was developed as a way to preserve vegetables during the harsh winter months when fresh produce was limited. Over the years, it has transformed into a vital food item and a representation of Korean culture and culinary traditions. The significance of kimchi in everyday Korean life is evident, as it is a common feature at every meal, often served as a side dish or included in main courses like kimchi jjigae (kimchi stew) or kimchi bokkeumbap (kimchi fried rice). The fermentation that gives kimchi its distinctive tang also adds to its health benefits, making it a key component of a diet rich in fermented foods.
The main health advantages of kimchi arise from its fermentation process, which introduces live probiotics—helpful microorganisms that promote gut health. Kimchi is abundant in lactic acid bacteria (LAB), such as Lactobacillus, Leuconostoc, and Pediococcus, all of which are vital for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. A well-functioning gut microbiome is crucial for effective digestion, nutrient absorption, and a strong immune system. Studies indicate that regularly eating fermented foods like kimchi can boost the diversity of gut microbiota, fostering the growth of beneficial bacteria while limiting harmful pathogens. This balance of microbes not only aids digestion but also enhances overall health. Research has shown that consuming kimchi increases the presence of Lactobacillus species in the gut, which is linked to better intestinal health and a lower risk of gastrointestinal issues.
Beyond its probiotic benefits, kimchi is packed with vitamins and bioactive compounds that enhance its health advantages. It is particularly rich in vitamin C, an antioxidant essential for immune health, as it helps shield the body from oxidative stress and aids in collagen production for maintaining healthy skin and repairing tissues. Additionally, kimchi is a good source of carotenoids, especially beta-carotene, known for its antioxidant effects that protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. The fermentation process also boosts the availability of certain nutrients. For instance, the fermented cabbage, which is the primary ingredient in kimchi, contains glucosinolates that have been linked to cancer prevention by supporting detoxification and improving the body’s ability to counteract harmful substances. Furthermore, the garlic and ginger commonly found in kimchi add to its health benefits, as both are recognized for their anti-inflammatory and immune-enhancing properties.
Kimchi plays a significant role in supporting gut health, which is closely connected to the immune system. Often called the "second brain," the gut contains a complex network of neurons and is essential for managing the body’s immune responses. Increasing research suggests that a healthy gut microbiome is crucial for optimal immune function. As a fermented food, kimchi is rich in probiotics that can influence immune responses positively. These probiotics have been found to boost the production of immunoglobulin A (IgA), an important antibody for mucosal immunity that defends against infections in the gastrointestinal tract. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory benefits of kimchi may contribute to reducing various health concerns.
Recent research has explored the role of kimchi in weight management. Eating kimchi has been linked to lower body fat and enhanced metabolism. One study revealed that individuals who regularly included kimchi in their diet had reduced body fat percentages and better lipid profiles compared to those who did not consume it. The bioactive components in kimchi, particularly capsaicin from chili peppers, may contribute to increased fat oxidation and metabolic rates. Capsaicin is known to elevate thermogenesis, the process where the body burns calories to generate heat, aiding in weight loss and fat reduction. This makes kimchi a valuable addition to a balanced diet for those aiming to maintain a healthy weight.
In addition to its direct health advantages, kimchi significantly contributes to overall well-being. The intake of fermented foods like kimchi has been associated with enhanced mood and mental health. A healthy gut microbiome is linked to improved mental health outcomes, as the gut and brain communicate through the gut-brain axis. Studies indicate that the probiotics present in kimchi may help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression by affecting the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, which are crucial for mood regulation. Moreover, the high fiber content in kimchi supports healthy digestion, helping to prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements. Fiber is vital for gut health, as it nourishes beneficial gut bacteria, allowing them to flourish and maintain a balanced microbiome.
The increasing awareness of kimchi's health advantages has contributed to its rising popularity around the globe. Once primarily a staple of Korean cuisine, kimchi is now savored by many as people recognize the significance of gut health and the benefits of fermented foods for overall wellness. With ongoing research shedding light on kimchi's positive effects, nutritionists and health professionals are increasingly recommending its inclusion in diets centered around fermented foods.
In nations where kimchi is a dietary mainstay, like South Korea, it is cherished not just for its flavor but also for its potential to enhance longevity. South Korea boasts one of the highest life expectancies worldwide, and some studies indicate that the regular consumption of fermented foods such as kimchi may play a role in this impressive health statistic.
kimchi is far more than just a tasty meal enhancer; it is a powerful, nutrient-rich superfood that offers numerous health benefits. From aiding gut health and strengthening the immune system to assisting with weight management and enhancing mental wellness, kimchi is a vital part of a healthy, fermented food-focused diet. As the global community increasingly recognizes the health benefits of probiotics and fermented foods, kimchi emerges as one of the most effective and accessible choices for improving overall health and supporting longevity. Its deep-rooted history, cultural importance, and exceptional nutritional value make kimchi not only a key element of Korean cuisine but also a significant addition to diets worldwide.
Sauerkraut: A Zesty Fermented Vegetable Packed with Probiotics
Sauerkraut is a classic fermented dish made from finely chopped cabbage, and it has been a key part of diets across various cultures for centuries. Its roots trace back to Europe, especially Germany, where it has been enjoyed for over two millennia. The term "sauerkraut" comes from the German words "sauer," which means sour, and "kraut," meaning cabbage, perfectly capturing its distinctive tangy taste.
The creation of sauerkraut involves a natural lactic acid fermentation process that transforms cabbage into a nutritious food packed with probiotics, enzymes, and vitamins, elevating it beyond just a tasty meal accompaniment. As we explore the history, ingredients, and health advantages of sauerkraut, it becomes clear why this humble dish has remained popular and is revered for its vital contributions to digestive health and overall wellness.
Fermentation has been a time-honored method for food preservation for thousands of years. In the case of sauerkraut, naturally occurring bacteria on cabbage leaves, such as Lactobacillus species, convert the sugars in the cabbage into lactic acid. This process not only preserves the cabbage but also boosts its nutritional value.
The lactic acid serves as a natural preservative, inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria. Additionally, fermentation fosters an ideal environment for beneficial bacteria, or probiotics, to flourish. These probiotics are essential for gut health, helping to maintain a balanced gut microbiome. As a rich source of probiotics, sauerkraut offers a simple and effective way to introduce these beneficial microorganisms into your digestive system.
One of the key health advantages of sauerkraut is its rich probiotic content. Probiotics are known to improve gut health by fostering a balanced environment of bacteria in the intestines. A well-balanced gut microbiome is crucial for effective digestion, nutrient absorption, and a robust immune system.
Studies have shown that the probiotics present in sauerkraut, especially Lactobacillus species, can enhance digestion, minimize bloating, and relieve constipation. By supporting the gut microbiome, sauerkraut may also help prevent and manage gastrointestinal issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Additionally, the probiotics in sauerkraut are associated with improved immune function, as a healthy gut microbiome is vital for regulating the immune system, warding off infections, and reducing inflammation.
Beyond its probiotic benefits, sauerkraut is packed with essential nutrients. It is a fantastic source of Vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that bolsters the immune system and protects cells from oxidative damage. The fermentation process helps to maintain and even boost the Vitamin C levels in cabbage, making sauerkraut an excellent choice for enhancing immunity, particularly during cold and flu seasons.
Sauerkraut is also high in fiber, which aids digestion and promotes heart health by helping to manage cholesterol levels. The fiber content can also promote a sense of fullness, making it a beneficial option for those looking to manage their weight. Furthermore, sauerkraut contains important minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which are essential for bone health, muscle function, and overall cellular health.
Sauerkraut contributes to digestive health in ways that go beyond just its probiotic properties. The fermentation process generates helpful enzymes that assist in breaking down and absorbing nutrients. These enzymes can enhance the body's ability to digest food more effectively and alleviate issues related to poor digestion, such as bloating and gas. Traditionally, sauerkraut has been used to treat indigestion and is known to improve the digestion of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Additionally, its high fiber content serves as a prebiotic, feeding the beneficial bacteria in the gut and promoting the growth of probiotics.
Another significant advantage of sauerkraut is its potential to benefit cardiovascular health. Studies indicate that fermented foods like sauerkraut may help lower blood pressure and decrease cholesterol levels. The bioactive compounds formed during fermentation, including peptides, may aid in promoting vasodilation and enhancing blood circulation, which can help prevent high blood pressure and lower the risk of heart disease. Furthermore, the fiber in sauerkraut can help reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol, further contributing to heart health.
Sauerkraut plays a significant role in supporting immune health, making it a worthy addition to your diet. A large part of the immune system resides in the gut, and maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is essential for optimal immune function. The probiotics found in sauerkraut can enhance the gut's protective barriers, boost the production of antimicrobial peptides, and stimulate immune cell activity. This positions sauerkraut as not just a beneficial digestive aid, but also a vital contributor to overall immune wellness. Additionally, the Vitamin C present in sauerkraut supports the production and function of white blood cells, which are crucial for combating infections.
Despite its numerous advantages, sauerkraut is frequently overlooked in contemporary diets, likely due to the prevalence of processed foods that lack the nutritional benefits of fermented options. However, as more people recognize the significance of gut health, fermented foods like sauerkraut are experiencing a resurgence. The growing interest in probiotics has led to a renewed appreciation for sauerkraut, celebrated not only for its deliciously tangy taste but also for its potential health benefits. As a fermented food, sauerkraut serves as a natural and nutrient-rich alternative to processed options that often miss out on the beneficial bacteria necessary for a healthy gut microbiome.
To fully enjoy the advantages of sauerkraut, it's important to select unpasteurized options, as pasteurization eliminates the valuable probiotics and enzymes. The ideal choices for maximizing health benefits are homemade sauerkraut or raw, unpasteurized varieties from the store. Additionally, like with any food, moderation is crucial. While sauerkraut is packed with nutrients, it also contains a significant amount of sodium, which may be a concern for those with high blood pressure or on a low-sodium diet. Therefore, it's vital to include sauerkraut in a balanced diet and consume it in moderation.
Sauerkraut is not just a zesty addition to meals; it is a nutritional powerhouse. Loaded with probiotics, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, it aids digestive health, strengthens the immune system, and enhances overall wellness. As a fermented food, it provides a natural method to improve the gut microbiome and boost nutrient absorption. Whether enjoyed as a side dish or used in various recipes, sauerkraut is a flexible and nutritious component of any diet. By embracing the art of fermenting cabbage, we can access the many benefits of sauerkraut and explore the rich, probiotic-filled realm of fermented foods.
Kefir: The Fermented Dairy Drink That’s Taking Over:
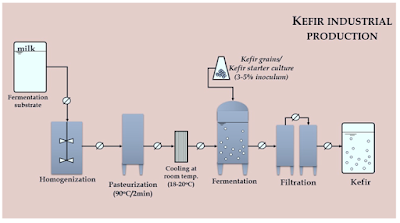
Kefir, a fermented dairy drink, has recently garnered considerable interest due to its impressive probiotic properties and health advantages. This beverage has its roots in the Caucasus Mountains of Eastern Europe and Southwestern Asia, where it has been enjoyed for thousands of years. The term "kefir" is thought to derive from the Turkish word "keyif," meaning "good feeling," which reflects its reputation for enhancing well-being. Traditionally, kefir is produced by fermenting cow, goat, or sheep milk with kefir grains—small, gelatinous clusters of bacteria and yeast. It has long been a staple in the diets of countries like Russia, Georgia, and Turkey. In recent years, kefir's appeal has expanded worldwide as a health-focused drink, particularly due to its abundant probiotics and potential benefits for gut health, digestion, and immune support.
Kefir is distinct from other fermented dairy products, such as yogurt, in several key aspects. Although both are created through milk fermentation, the processes and microorganisms involved differ significantly. Yogurt is produced using specific bacterial strains, primarily Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, which convert lactose into lactic acid, giving yogurt its signature tangy flavor.
In contrast, kefir is fermented with a mix of bacteria and yeast, resulting in a more diverse microbial profile. This unique fermentation method leads to a richer and more varied array of probiotics, including strains from the Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Saccharomyces families. This variation in microbial composition is what sets kefir apart as a particularly powerful source of probiotics, providing a wider range of beneficial microorganisms compared to yogurt.
One of the key health advantages of kefir is its capacity to enhance gut health. The probiotics found in kefir are essential for maintaining a balanced gut microbiome, which is vital for effective digestion and overall well-being. This microbiome consists of trillions of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that collaborate to break down food, absorb nutrients, and defend against harmful pathogens. A disruption in the balance of these microbes can result in digestive problems like bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Kefir aids in restoring this balance by introducing a diverse range of beneficial bacteria into the gut, thereby enhancing the microbiome's diversity and supporting its optimal performance. Research indicates that regularly consuming kefir can alleviate symptoms of digestive discomfort, such as bloating and irregular bowel habits, and may even assist with conditions like IBS and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Beyond its probiotic properties, kefir is also abundant in bioactive compounds that promote overall health. One notable compound is kefiran, a polysaccharide present in kefir grains, known for its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and immune-enhancing effects. Kefiran helps shield the body from harmful bacteria and may encourage a healthy inflammatory response.
This is particularly significant, as chronic inflammation has been associated with various health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. By mitigating inflammation in the gut and other areas of the body, kefir may offer protection against these conditions. Additionally, kefir is packed with essential nutrients such as calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and B vitamins, which are crucial for bone health, energy metabolism, and overall cellular function.
One of the most persuasive reasons to add kefir to your diet is its ability to support the immune system. The immune system is closely linked to gut health, as a significant number of the body's immune cells are located in the digestive tract. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is vital for the immune system to function properly, and the probiotics in kefir enhance this by promoting the production of beneficial immune cells.
Research has demonstrated that kefir's probiotics can boost the creation of white blood cells, which are essential for combating infections. Additionally, kefir has been shown to enhance the activity of natural killer cells, a type of immune cell crucial for defending against viruses and cancer. By strengthening the immune system in this manner, kefir can help shield the body from infections, lessen the severity of illnesses, and promote overall immune health.
The advantages of kefir go beyond just digestive health and immunity; it may also play a role in mental health and wellness. Increasing evidence suggests a link between gut health and mental well-being, often referred to as the "gut-brain axis." This connection indicates that a healthy gut microbiome can positively affect brain function, mood, and mental health. Probiotics found in kefir may help enhance mood, alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety, and improve cognitive function. Some studies have indicated that consuming kefir and other fermented foods can lead to better mental health, potentially by reducing inflammation and supporting the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, which are crucial for mood regulation.
Kefir can be beneficial for those aiming to enhance their skin health. Thanks to its rich probiotic content, it may assist with various skin issues like acne, eczema, and rosacea. Probiotics play a role in regulating the skin's immune system and can help reduce inflammation associated with these conditions. Moreover, the lactic acid bacteria found in kefir are believed to support a balanced skin microbiome by preventing the growth of harmful bacteria that can lead to skin problems. Additionally, kefir contains antioxidants such as Vitamin E and selenium, which may protect the skin from oxidative stress, contributing to a vibrant and youthful look.
However, kefir does have some potential downsides. While it is generally safe for most individuals, those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies might experience digestive issues or allergic reactions. It's important to note that the fermentation process in kefir reduces much of the lactose, making it more digestible for many lactose-intolerant individuals. There are also non-dairy kefir options made from coconut, almond, or soy milk, which can be great alternatives for those who cannot consume dairy. As with any food, it's best to enjoy kefir in moderation, as consuming too much may lead to digestive discomfort, especially for those who are not used to high levels of probiotics.
Kefir has gained significant popularity in recent years, largely due to the increasing focus on gut health and the advantages of probiotics. As more people recognize the significance of the gut microbiome, kefir has become a common choice in many health-oriented diets. It is readily available in grocery stores, health food shops, and online, offering a range of flavors and formulations to cater to various preferences and dietary requirements. Kefir can be enjoyed on its own, blended into smoothies, or used as a base for salad dressings, sauces, and even baked goods. Its adaptability and remarkable health benefits make it a delightful and simple addition to any diet.
kefir is a potent, nutrient-dense fermented drink that provides numerous health advantages. Packed with powerful probiotics, bioactive compounds, and vital nutrients, kefir promotes gut health, aids digestion, boosts immunity, and even enhances mental well-being. Its distinct microbial profile differentiates it from other fermented dairy products like yogurt, making it a valuable choice for those looking to enhance their health. Whether enjoyed as a daily drink or included in various recipes, kefir is a fantastic way to leverage the benefits of probiotics and support overall wellness.
Kombucha: The Fizzy Fermented Tea Known for Its Gut-Health Benefits
Kombucha, a fizzy and fermented tea, has gained immense popularity in recent decades, attracting health enthusiasts globally. With its unique tang and effervescent quality, kombucha has transitioned from a niche item to a widely available beverage in supermarkets, cafes, and health food stores. Its roots can be traced back over two millennia to East Asia, where it is believed to have originated in China. According to legend, an emperor during the Qin Dynasty discovered kombucha while searching for a drink that promised immortality. The term "kombucha" is thought to be derived from "Kombu," a Japanese doctor credited with introducing the tea to the emperor. From China, kombucha made its way to Japan and Russia, where it became renowned for its alleged health benefits. Nowadays, it is celebrated in global markets for its contributions to digestive health, detoxification, and natural energy enhancement.
At its essence, kombucha is created by fermenting sweetened tea with a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY), which resembles a gelatinous mushroom. The fermentation process starts with brewing tea, typically black or green, and adding sugar. The SCOBY is then introduced to the sweetened tea, where it begins to consume the sugar, converting it into alcohol, acetic acid, and various other compounds, including vitamins, minerals, and organic acids.
Over several days, the tea undergoes fermentation, resulting in a bubbly, tangy drink. The final product is rich in beneficial microorganisms, such as probiotics, which are vital for gut health. Additionally, the fermentation process yields a small amount of alcohol, usually under 0.5% by volume, which is not enough to induce intoxication but adds to the drink's unique flavor.
The health advantages of kombucha mainly stem from its probiotic content, which arises during the fermentation process. Probiotics are beneficial microorganisms that are vital for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, crucial for effective digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune system health. A well-balanced gut microbiome helps control harmful bacteria, enhances food digestion, and aids in the production of essential vitamins and minerals. Studies indicate that the probiotics found in kombucha, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, can improve digestion and relieve gastrointestinal discomforts like bloating, gas, and constipation. By fostering the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, kombucha contributes to a balanced microbial environment, promoting overall digestive wellness.
Beyond its probiotic benefits, kombucha is recognized for its detoxifying qualities. The fermentation process generates various organic acids, including acetic, gluconic, and glucuronic acids, which assist in detoxification. Notably, glucuronic acid is thought to bind with toxins and heavy metals in the body, helping to eliminate them through the kidneys. This detoxifying property is a key reason kombucha is often referred to as a "cleanse" beverage.
It is believed to support liver function and facilitate the body's natural detoxification processes by aiding in the removal of harmful substances. Additionally, the presence of polyphenols—potent antioxidants found in tea—further boosts kombucha's detoxifying effects. These antioxidants work to neutralize free radicals in the body, safeguarding cells from oxidative stress and inflammation that can lead to chronic illnesses.
Kombucha is highly valued for its energy-boosting properties, largely thanks to the small amounts of caffeine and B vitamins it contains. The tea used for brewing kombucha, typically black or green tea, has caffeine, a natural stimulant that enhances mental clarity and alertness. Although the fermentation process reduces the caffeine content somewhat, there is still enough left to provide a gentle energy lift without the jitteriness often linked to coffee.
Additionally, kombucha is abundant in B vitamins, such as B1 (thiamine), B6 (pyridoxine), B12 (cobalamin), and biotin, all of which are vital for energy production and metabolism. These B vitamins assist in converting food into usable energy, support the nervous system, and improve the body’s response to stress. Consequently, many people who drink kombucha report feeling more energized and focused, making it a favored alternative to sugary energy drinks and coffee.
Another notable advantage of kombucha is its potential to enhance immune health. A healthy gut microbiome, supported by the probiotics found in kombucha, is crucial for a robust immune system. A well-balanced gut microbiome can improve the body’s ability to combat infections and lower inflammation, both of which are vital for optimal immune function. Research indicates that the probiotics in kombucha can boost the production of immune cells, such as macrophages and lymphocytes, which play a key role in protecting the body from pathogens. Moreover, the antioxidants present in kombucha, especially those from the tea, may help alleviate oxidative stress, which can compromise the immune system and heighten the risk of chronic illnesses. By promoting gut health and minimizing inflammation, kombucha contributes to strengthening the body’s natural defenses.
Kombucha offers a range of health benefits that extend beyond just supporting the digestive and immune systems. Studies indicate that it may also positively influence cardiovascular health. The fermentation process produces organic acids, especially acetic acid, which is thought to help lower cholesterol levels by inhibiting its production in the liver. Furthermore, the antioxidants found in kombucha can protect blood vessels from damage caused by free radicals, which are linked to atherosclerosis and other heart-related issues. Some research even suggests that kombucha may assist in regulating blood pressure, providing additional support for heart health. Although further studies are necessary to fully grasp the impact of kombucha on cardiovascular wellness, the initial results are encouraging.
Beyond its health advantages, kombucha is a versatile drink that can be tailored to individual preferences. Its flavor profile varies based on the type of tea used, the fermentation duration, and any additional flavorings or infusions added afterward. Common flavor enhancements include ginger, lemon, berries, and various herbs, which not only improve the taste but also contribute to its health benefits. The natural fizz of kombucha, a byproduct of fermentation, adds a refreshing and enjoyable element to the beverage. As its popularity continues to rise, new flavors and variations are regularly being introduced, enhancing its appeal even further.
While kombucha boasts numerous health advantages, it also has some potential downsides. Its acidic composition can lead to digestive issues for those with sensitive stomachs or individuals who experience acid reflux. Furthermore, since kombucha contains a trace amount of alcohol, it's advisable for those who are alcohol-sensitive or pregnant to enjoy it in moderation. Generally, kombucha is safe for most people, but it's wise to consult a healthcare professional before making any major dietary changes, especially for those with existing health concerns.
kombucha is a nutritious and beneficial fermented drink that provides a variety of advantages, such as enhanced digestion, detoxification, increased energy, and immune support. Packed with probiotics, organic acids, antioxidants, and B vitamins, kombucha serves as a valuable asset for promoting overall health and wellness. As more people recognize the significance of gut health, the popularity of kombucha is expected to continue growing. Whether enjoyed as a refreshing drink or incorporated into different recipes, kombucha offers a natural and effective means to foster a healthy lifestyle.
All rights reserved by Bubble Organic © 2026